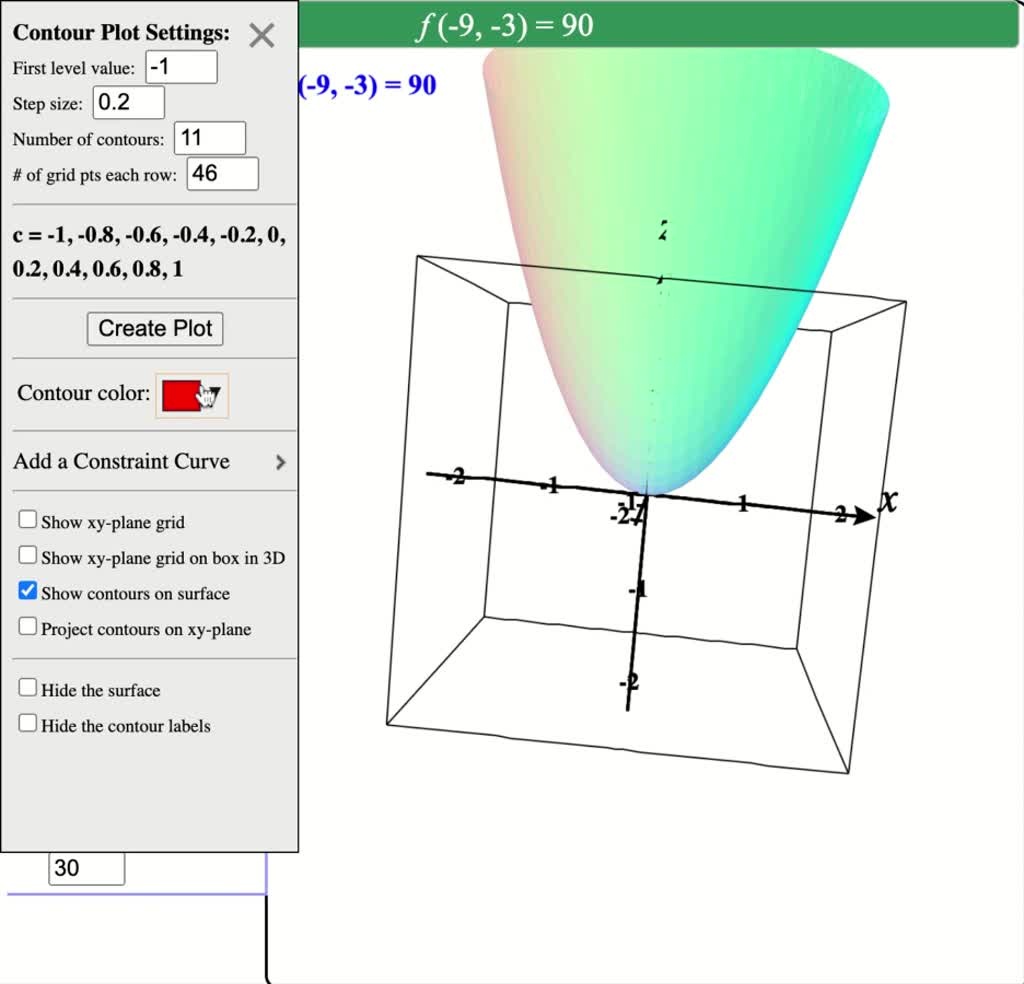
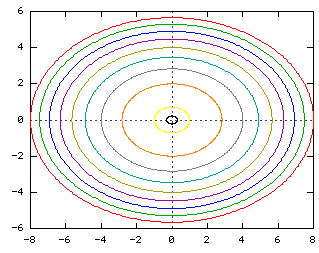
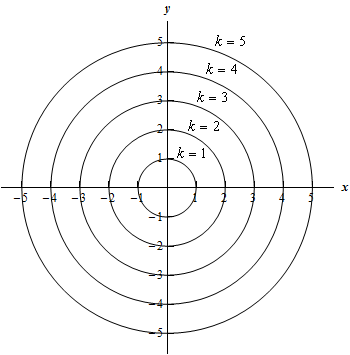
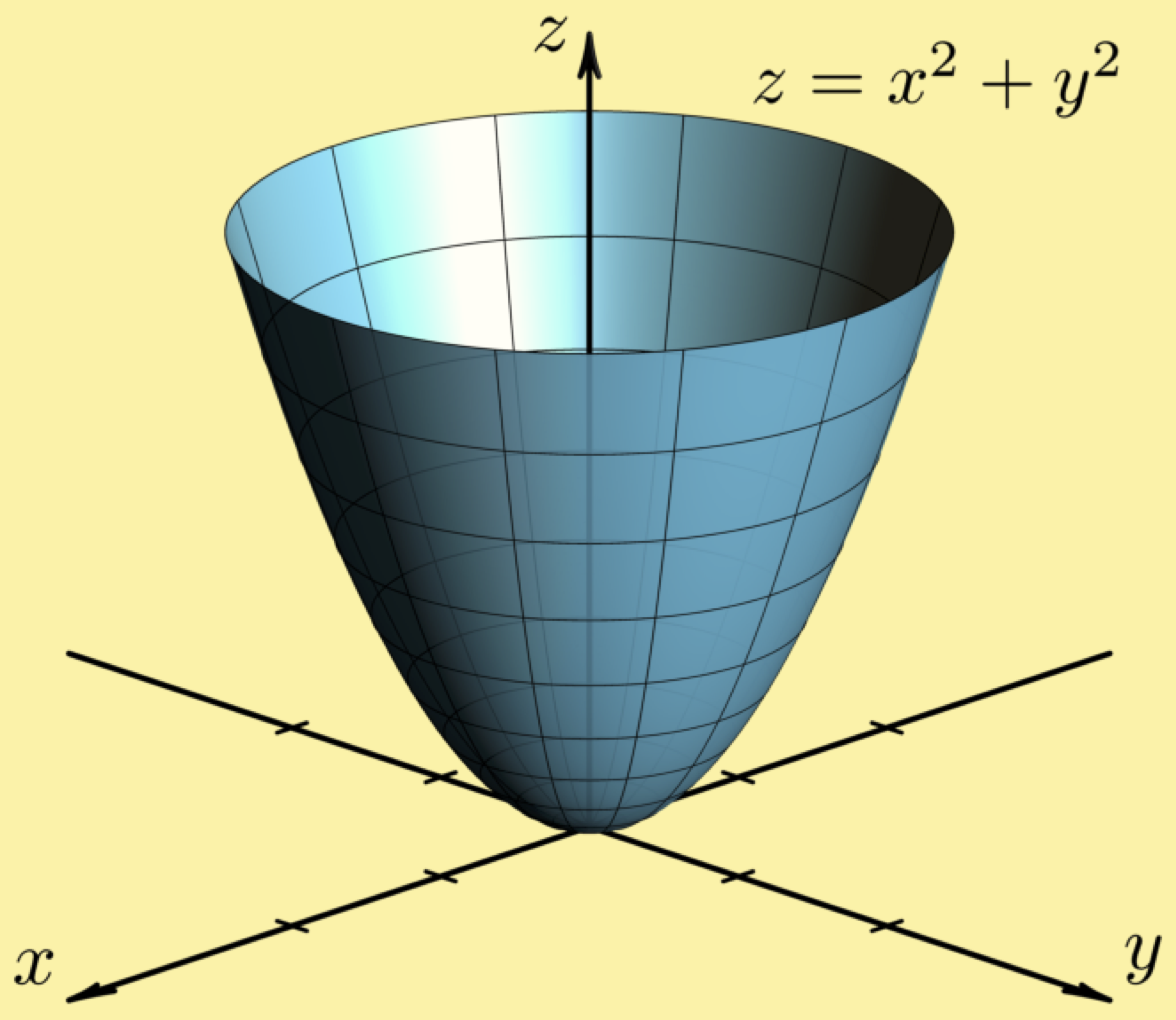
Sketch several traces or level curves of a function of two variables equation describes a circle with radius centered at the point Therefore the range of is The graph of is also a paraboloid, and this paraboloid points downward as shownAccording to the internet, finding the circumference of paraboloid level curves seemed a tad too easy It said to simply plug in the z value or the height level into the formula c = x^2 y^2 or something like that, square root the c value to get the level curve circles radius For example at z = 1 the circles radius would be square root 1 aka 1Answer I'll give you two parameterizations for the paraboloid x^2y^2=z under the plane z=4 Parameterization 1 Perhaps the easiest way to parameterize the paraboloid is to just let x=u and y=v Then, since z is already expressed in terms of x and y,
Solved Describe In Words The Level Curves Of The Paraboloid Z X 2 Y 2
Elliptic paraboloid level curves
Elliptic paraboloid level curves- The level curves are parabolas of the form y2Zo ;Multivariable Functions, Surfaces, and Contours – HMC Calculus Tutorial The graphs of surfaces in 3space can get very intricate and complex!



Level Sets Ximera
Level Curves of a Paraboloid This example requires WebGL Visit getwebglorg for more info When we lift the level curves up onto the graph, we get "horizontal traces" Describe in words the level curves of the paraboloid z = x2 y2 Choose the correct answer below A The level curves are parabolas of the form x2 = zo B The level curves are lines of the form x y = C The level curves are parabolas of the form y2 = zo D The level curves are circles of the form x2 y2 = 2oA level curve of a function f(x,y) is the curve of points (x,y) where f(x,y) is some constant value, on every point of the curve Different level curves produced for the f(x,y) for different values of c can be put together as a plot, which is called a level curve plot or a contour plot
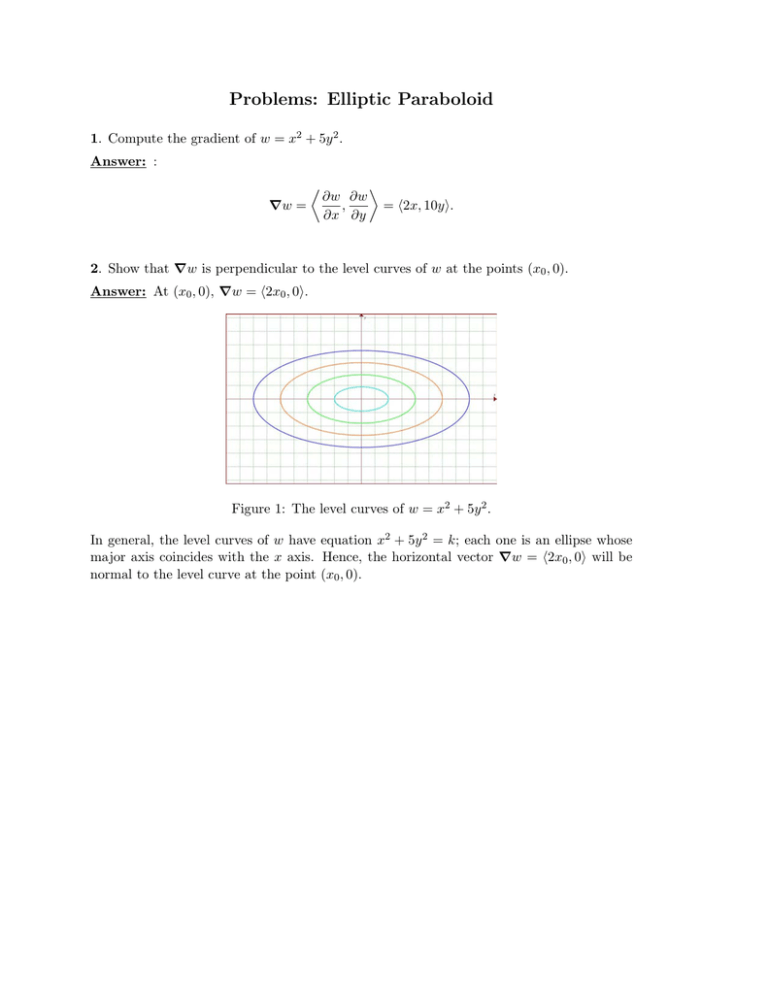
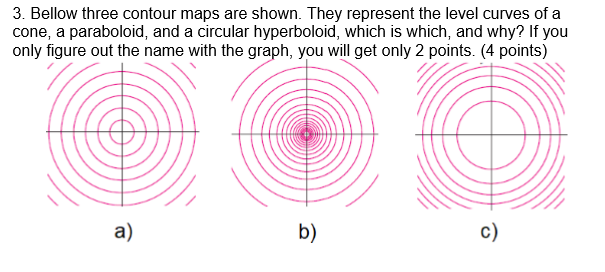
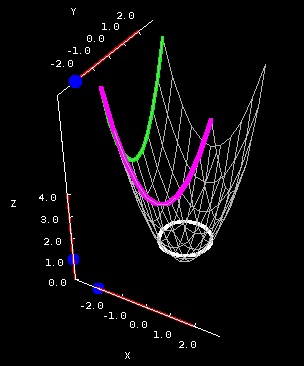
EXAMPLE 11 Graph the function 2 2 ( ,) 100 f x y x y =in space and plot the level curves ( ,) 0 f x y =, ( ,) 51 f x y = a nd ( ,) 75 f x y = in the domain of f in the plane Solution The domain of f is the entire x yplane and the range of f is the set of real numbers less than or equal to 100 The graph is the paraboloid 2 2 100 z x yPlotting Level Curves of an Elliptic Paraboloid Plotting Level Curves of an Elliptic ParaboloidEach one is an ellipse whose major axis coincides with the x axis Hence, the horizontal vector Vw = (2x 0, 0) will be normal to the level curve at the point (x 0, 0)
Two Model Examples Example 1A (Elliptic Paraboloid) Consider f R2!R given by f(x;y) = x2 y2 The level sets of fare curves in R2Level sets are f(x;y) 2R 2 x y2 = cg The graph of fis a surface in R3Graph is f(x;y;z) 2R3 z= x2 y2g Notice that (0;0;0) is a local minimum of fThe Gradient Vector – GeoGebra Materials The gradient at each point is a vector pointing in the ( x, y) plane You compute the gradient vector, by writing the vector ∇ F = ∂ F ∂ x 1, ∂ F ∂ x 2, , ∂ F ∂ x n You've done this sort of direct computation many times before SoA graph of some level curves can give a good idea of the shape of the surface;




Level Curve And A Surface Tex Latex Stack Exchange



Problems Elliptic Paraboloid
The level curves in this case are just going to be lines So, for instance, if we take the level curve at z equals 0, then we have just the equation 2x plus y equals 0 And so that has interceptso we're looking atso 0 equals 2x plus y, so that's just y equals minus 2x So that's this level curve That's the level curve at z equals 0Figure 961 The graph of a curve in space Thus, we can think of the curve as a collection of terminal points of vectors emanating from the origin We therefore view a point traveling along this curve as a function of time \(t\text{,}\) and define a function \(\vr\) whose input is the variable \(t\) and whose output is the vector from the origin to the point on the curve at time \(t\text{}\)Functions of Several Variables Calculus Early Transcendentals 3rd Edition Chapter 15 Functions of Several Variables Section 1 Graphs and Level Curves



Hyperbolic Paraboloid With Level Curves M3dp Net



Level Curves Functions Of Several Variables By Openstax Page 3 12 Jobilize
Figure 1 The level curves of w = x 2 5y 2 In general, the level curves of w have equation x 2 5y 2 = k;Would call these contours, but we call them level curves To nd a level curve, you just choose a height z = c and then write down the equation f(x;y) = c, where f(x;y) is the formula for the original function For example, for the function z = x 2 y2, level curves are the graphs of x y2 = c, for various values of c If c > 0, then these curvesLevel curves are obtain by taking the horizontal traces of a function of several variables and projecting them into the xyplane We have already seen that the level curves of the elliptic paraboloid



Math Bu Edu



Math 0 Theory
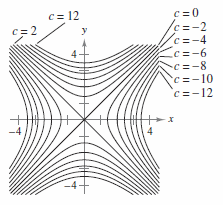
Plot the contour plot (level curves) of the same hyperbolic paraboloid > contourplot( f, x = 4 4, y = 4 4, scaling = constrained ) ;Describe in words the level curves ofthe paraboloid z = x y Choose the correct answer below The level curves are lines of the form x y = zo The level curves are parabolas of the form x The level curves are circles of the form x y The level curves are parabolas of the form y Find the domain of the following function g(x,y) = In (x 7 — y)Mathematics Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for people studying math at any level and professionals in related fields It only takes a minute to sign up



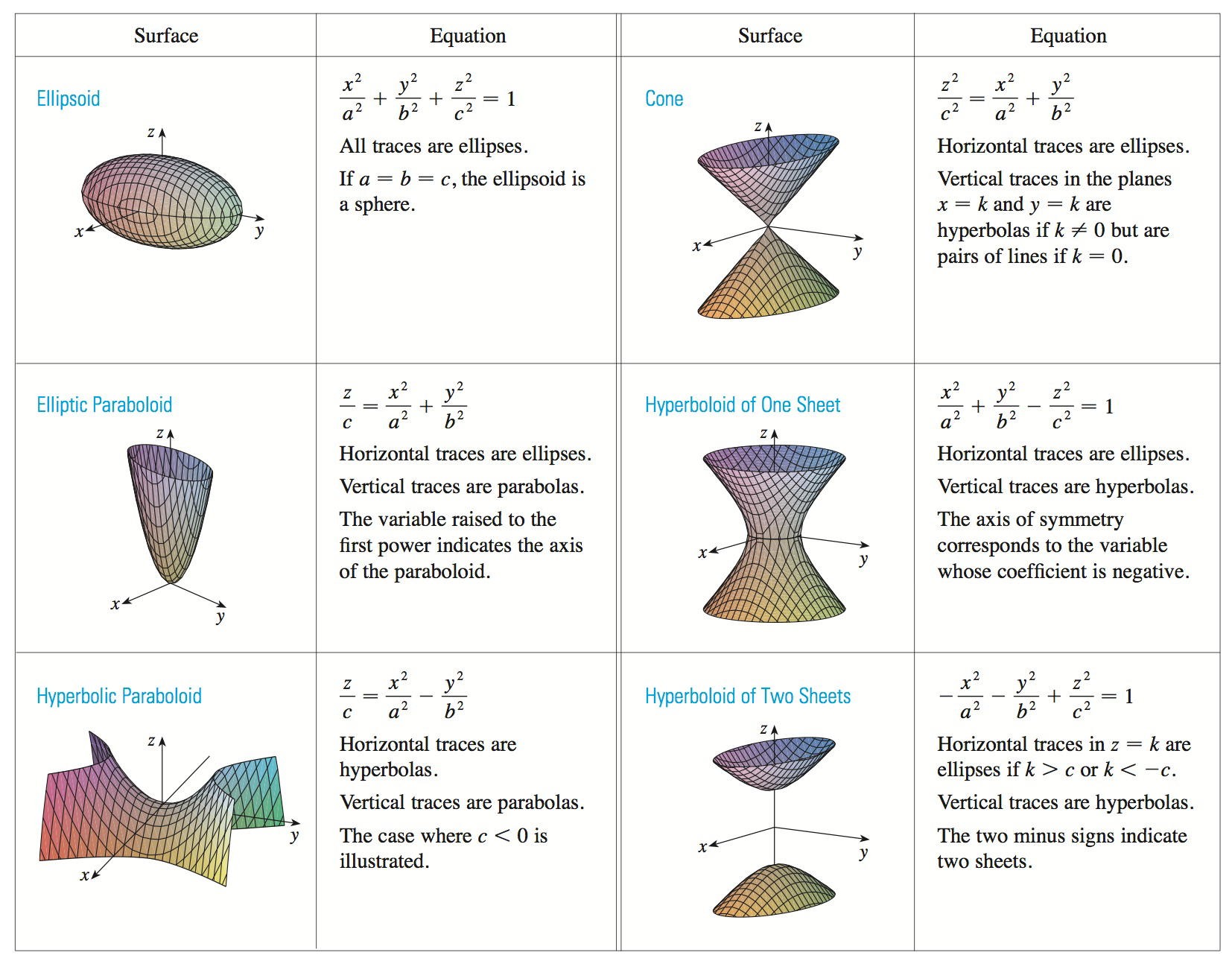
Solved 3 Bellow Three Contour Maps Are Shown They Chegg Com




Solved Describe In Words The Level Curves Of The Paraboloid Z X 2 Y 2
Example 8 Describe the level curves of g(x,y) = y2 − x2 from Examples 4 and 5 Answer Figures A8a and A8b • The level curves g = c is a hyperbola with the equation y 2− x = c (The surface is a "hyperbolic paraboloid") Level curves of g(x,y) = y2 −x2 Figure A8a Figure A8bLevel curves The two main ways to visualize functions of two variables is via graphs and level curves Both were introduced in an earlier learning module Level curves for a function z = f ( x, y) D ⊆ R 2 → R the level curve of value c is the curve C in D ⊆ R 2 on which f C = c Notice the critical difference between a level curve CAnalogically one can define the level surfaces (or contour surfaces) F (x, y, z) = c F ( x, y, z) = c (3) for a function F F of three variables x x, y y, z z The gradient of F F in a point (x, y, z) ( x, y, z) is parallel to the surface normal of the level surface passing through this point Title level curve



Calculus Iii Exam Iii Notes And Links Math Resources Vosbury V2 0



Contours Html
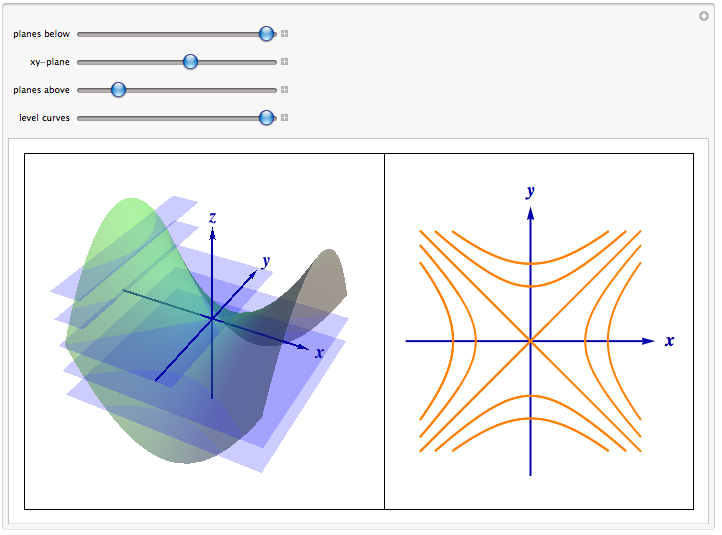
So consider for a paraboloid graph, whose level curves are circles, the gradient points radially outward from the origin The relationship between the two is shown in the next graph As the gradient, whose form for a paraboloid with a circular crosssection is 〈 〉, get closer to the origin they get shorter, and furtherElliptic Paraboloid 2 5 z2 = x2 y2 Circular Double Cone 6 x2 y2 z2 = 1 Hyperboloid of 1 Sheet 7 z = 4 x2 y2 Circular Paraboloid 3 8 3x2 4y2 6z2 = 12 Ellipsoid 9 4x 2 9y2 36z = 36 Hyperboloid of 2 Sheets 10 Identify each of the followingLevel curves and surfaces The level curves of are curves in the plane along which has a constant value We will sketch level curves corresponding to a couples values, such as The level set is given by , or This is a parabola in as a function of Now we add the and level sets




Solved 3 A Consider The Standard Hyperbolic Paraboloid S Z Chegg Com



14 1 Functions Of Several Variables
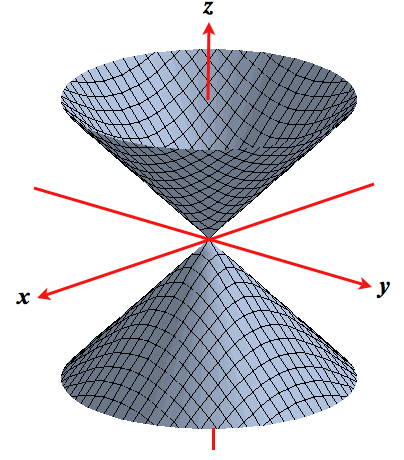
Given a function f(x,y), the set f(x,y) = c = const is called a contour curve or level curve of f For example, for f(x,y) = 4x2 3y2 the level curves f = c are ellipses if c > 0 Level curves allow to visualize functions of two variables f(x,y) = x2 y2 which is a paraboloid Note however that most surfaces of the form g(x,y,z) = c canSolution If I slice the cone with cuts parallel to the xyplane at even intervals (for example, at z= 1, z= 2, z= 3, etc), then the radius of the circles grow linearlyAnswer (1 of 5) A level curve can be drawn for function of two variable ,for function of three variable we have level surface A level curve of a function is curve of points where function have constant values,level curve is simply a cross section of graph of



Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables



1
Level Curves (ie Contours) and Level Surfaces Consider a function For any constant we can consider the collection of points satisfying the equation This collection of points is generally called a level surfaceWhen we generically have a (true 2dimensional) surface For example The level surface of at level is the unit sphere (the sphere of radius 1 centered at the origin)1 Level Surfaces 2 If one of the Arguments is time we can animate ie w = f(x,y,t) Level Surfaces Given w = f(x,y,z) then a level surface is obtained by considering w = c = f(x,y,z) The interpretation being that on a level surface f has the same value at every pt For example f could represent the temperature at each pt in 3space Solving for level curves of an elliptic paraboloid given by quadric surface equation Follow 18 views (last 30 days) Show older comments supernoob on 16 Jul (level curve) at a given height z, and to get the vertices of this ellipse It would be nice to plot the ellipse, too I have to do this over and over again, so the fastest way would




Why Is The Gradient Related To The Normal Vector To A Surface Continuous Everywhere But Differentiable Nowhere



The Movie Hyperbolic Paraboloid
C Graph the level curve AHe, iL=3, and describe the relationship between e and i in this case T 37 Electric potential function The electric potential function for two positive charges, one at H0, 1L with twice the strength as the charge at H0, 1L, is given by fHx, yL= 2 x2 Hy1L2 1 x2 Hy 1L2 a Graph the electric potential using the window @5, 5Dµ@5, 5Dµ@0, 10 DQuestion 1327 Describe in words the level curves of the paraboloid z=x y2 Choose the correct answer below A The level curves are lines of the form x y=Zo O B The level curves are circles of the form x2 y2 ° C The level curves are parabolas of the form x2Zo 0 DLevel curves Level curves for a function z = f ( x, y) D ⊆ R 2 → R the level curve of value c is the curve C in D ⊆ R 2 on which f C = c Notice the critical difference between a level curve C of value c and the trace on the plane z = c a level curve C always lies in the x y plane, and is the set C of points in the x y plane on




Answered X Y Level Curves Consider The Bartleby



Level Curves
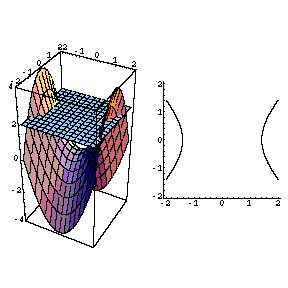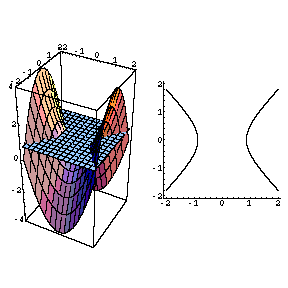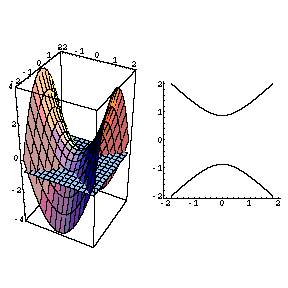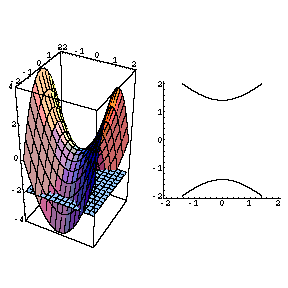
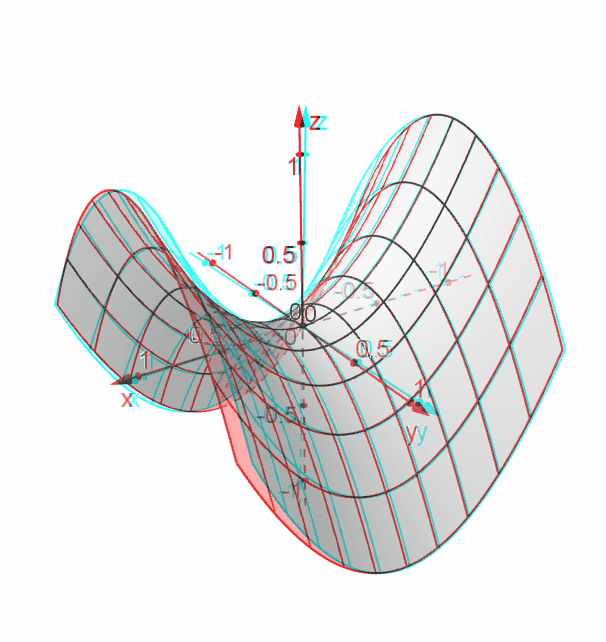
It looks much like a topographic map of the surface In figure 1412 both the surface and its associated level curves are shown Note that, as with a topographic map, the heights corresponding to the level curves are evenly spaced, so that where curves are closerThis surface is called a hyperbolic paraboloid because the traces parallel to the \(xz\) and \(yz\)planes are parabolas and the level curves (traces parallel to the \(xy\)plane) are hyperbolas The following figure shows the hyperbolic shape of a level curve To view the interactive graph Make sure you have the latest version of Java 7WolframAlpha Widgets "Level Curve Grapher" Free Mathematics Widget Level Curve Grapher Level Curve Grapher Enter a function f (x,y) Enter a value of c Enter a



The Elliptic Paraboloid Math Insight



2
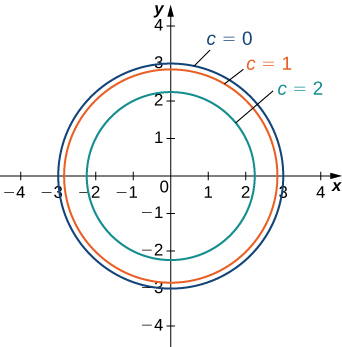
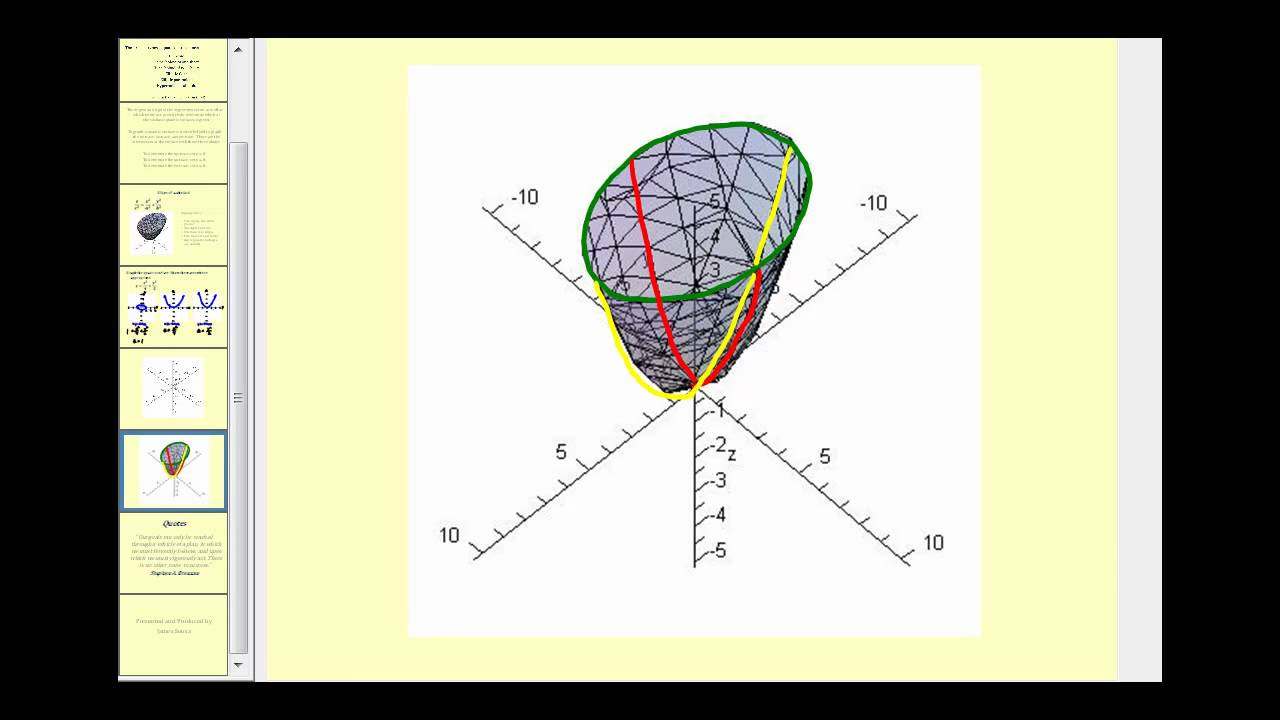
Scroll down to the bottom to view the interactive graph This graph illustrates the transition from a hyperboloid of one sheet to a hyperboloid of two sheets Consider the equation x 2 y 2 − z 2 = C In case if C > 0, the level curves x 2 y 2 = C k 2 are circles at any level z = k Therefore, the surface continues from negative z to2The level curves for the cone (graph ~) and the paraboloid (graph }) are both concentric circles How did you determine which set of level curves match the cone?In mathematics, a parabola is a plane curve which is mirrorsymmetrical and is approximately UshapedIt fits several superficially different mathematical descriptions, which can all be proved to define exactly the same curves One description of a parabola involves a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix)The focus does not lie on the directrix The parabola is the locus of points in
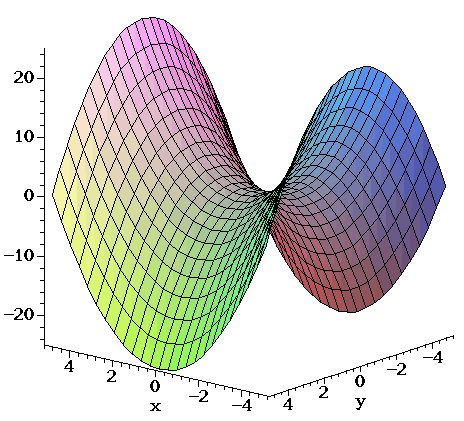



Surfaces Part 2



Level Curves And Contour Plots Mathonline
Level curves of a hyperbolic paraboloidCurves Circles The simplest nonlinear curve is unquestionably the circle A circle with center (a,b) and radius r has an equation as follows (x a) 2 (x b) 2 = r 2 If the center is the origin, the above equation is simplified to x 2 y 2 = r 2 The above equations are referred to as the implicit form of the circle The parametric form of Describe the level curves of the function z = 2x2 y2 1 for c = 0,2,3 Answer Ellipses 2 Sketch several level curves for the paraboloid z = 4 x2 y2 3 Describe the level surfaces of the function F(x, y, z) = 9 x2 y2 – 22 Answer Level surfaces are spheres x2 y2 z2 = p2 (0
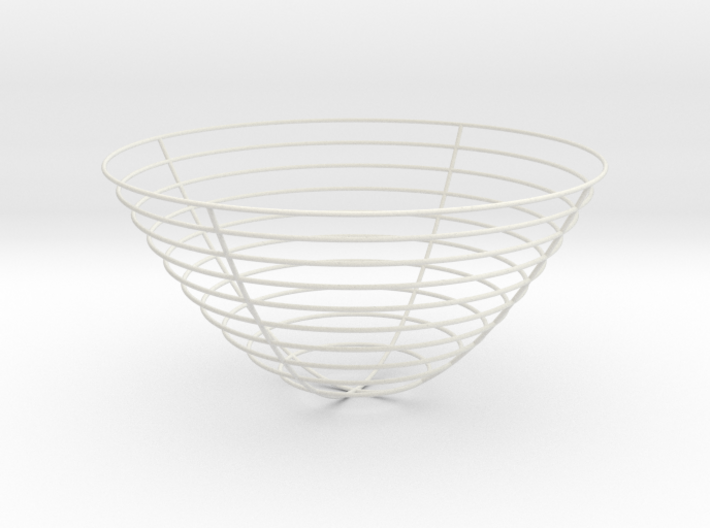




Paraboloid Level Curves 8 In Ubqe9xja8 By Bachman
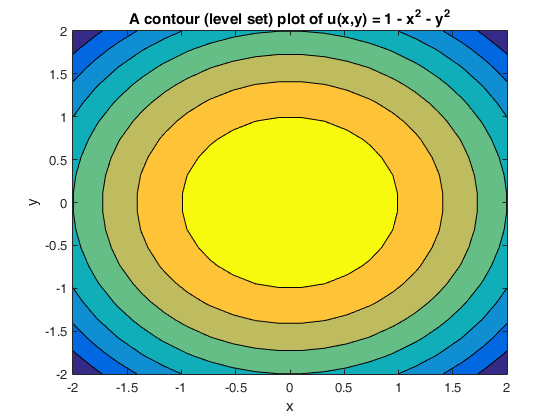



Howtoplotfunctiontwovariables
The level functions for paraboloid and the level function for ellipsoid are given This is what I've done so far I found the equation of the curve that forms from the intersection c(x,y) = curve of paraboloid and ellipsoid intersection The tangent vector at p(x1,y1,z1) on curve should be the same as the tangent vector at same point onIn this tutorial, we investigate some tools that can be used to help visualize the graph of a function f ( x, y), defined as the graph of the equation z = f ( x, y) Try plotting z = sin ( x y)!Obtain the monthly binned light curve is similar to those of weekly binned described above 32 Mets¨ahovi The 37 GHz observations were obtained with the 137 m diameter Mets¨ahovi radio telescope, which is a radome enclosed paraboloid antenna situated in Finland The measurements were made with a 1 GHzband dual beam receiver centred at 368




Functions Of Several Variables
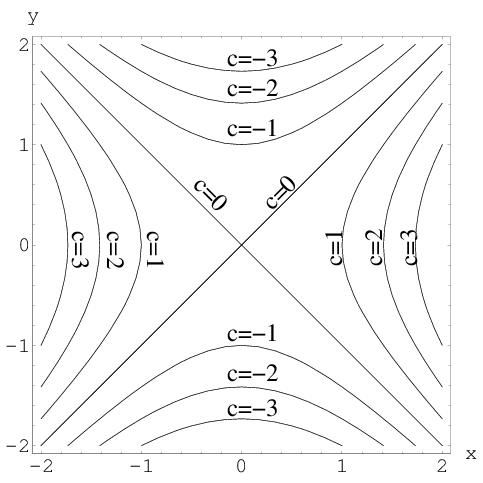



Image Level Curves Of A Hyperbolic Paraboloid Math Insight
The advantage of level curves over graphs is that you already have a lot of practice drawing curves in \(\R^2\), but you probably don't have much practice drawing surfaces in \(\R^3\) Here are some computer generated images of paraboloids, one elliptic (level curves are ellipses) and one hyperbolic (level curves are hyperbolas) This is an elliptic paraboloid and is an example of a quadric surface We saw several of these in the previous section The next topic that we should look at is that of level curves or contour curves The level curves of the function \(z = f\left( {x,y} \right)\) are two dimensional curves we get by setting \(z = k\), where \(k\) is any



Hyperbolic Paraboloid With Level Curves M3dp Net




Session 35 Gradient Definition Perpendicular To Level Curves Part B Chain Rule Gradient And Directional Derivatives 2 Partial Derivatives Multivariable Calculus Mathematics Mit Opencourseware
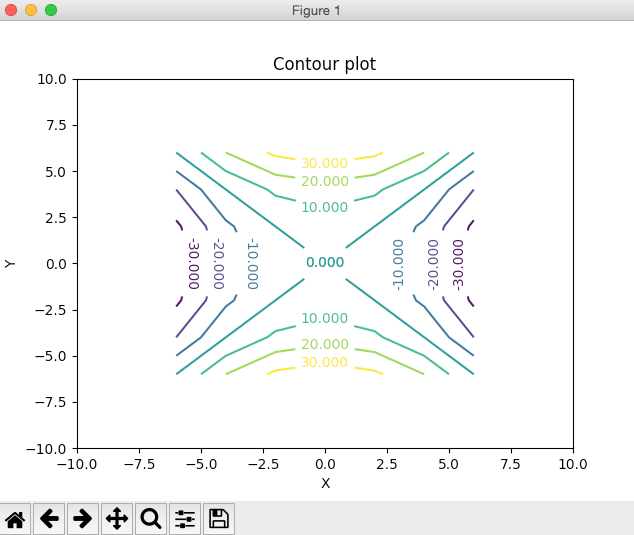



Contour Plot Using Python And Matplotlib Pythontic Com



The Gradient And Directional Derivative



Level Curves And Contour Plots Mathonline



1



Answer In Differential Geometry Topology For Shweta 1350
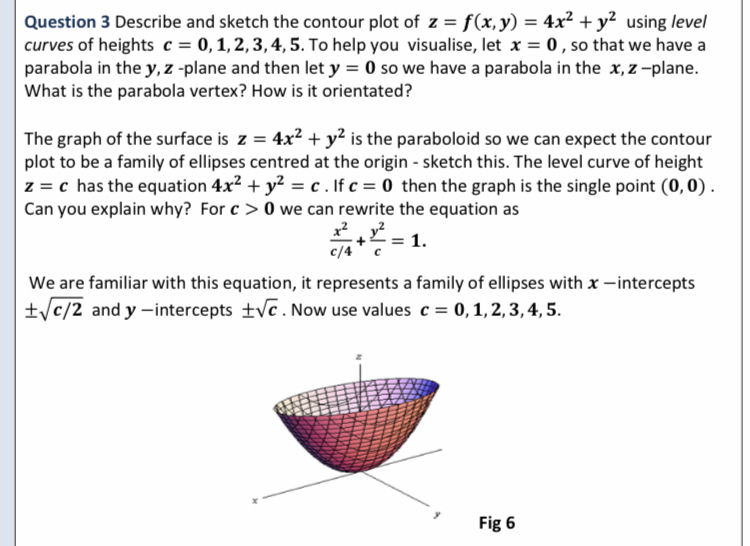



Answered Question 3 Describe And Sketch The Bartleby



Level Sets Ximera



Answer In Differential Geometry Topology For Runali 1356



0 3 Visualizing Functions Of Several Variables
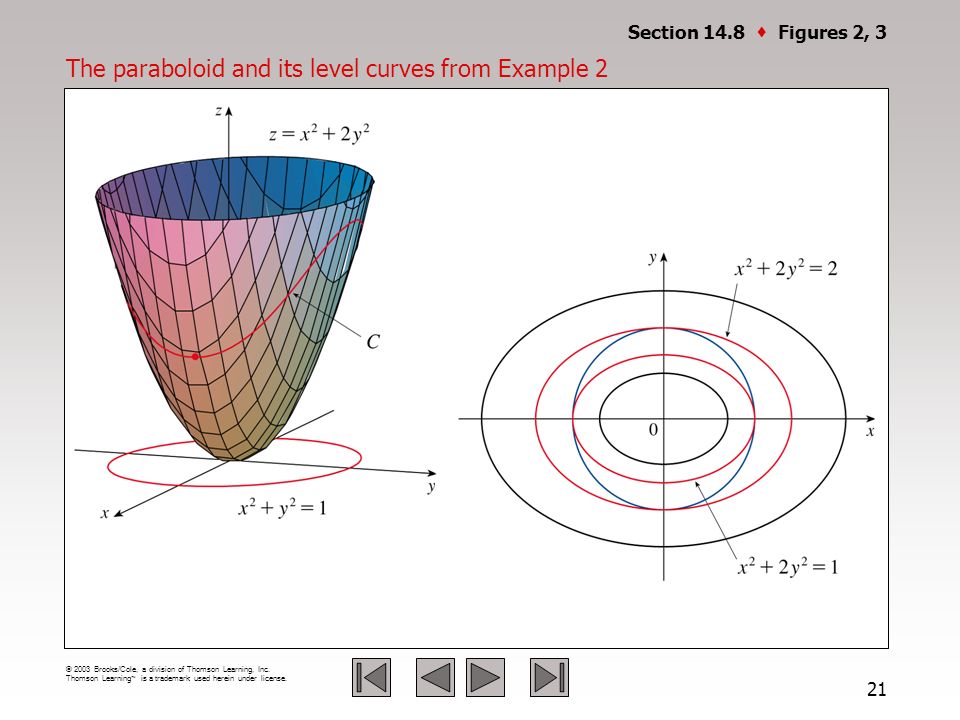



Chapter 14 Partial Derivatives Ppt Video Online Download
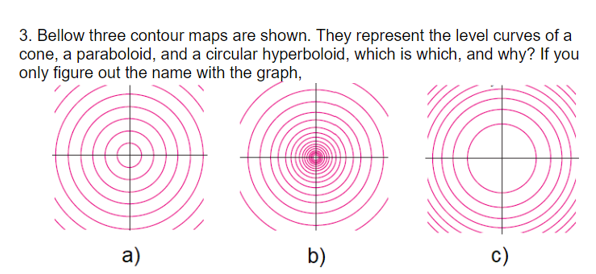



Solved 3 Bellow Three Contour Maps Are Shown They Chegg Com
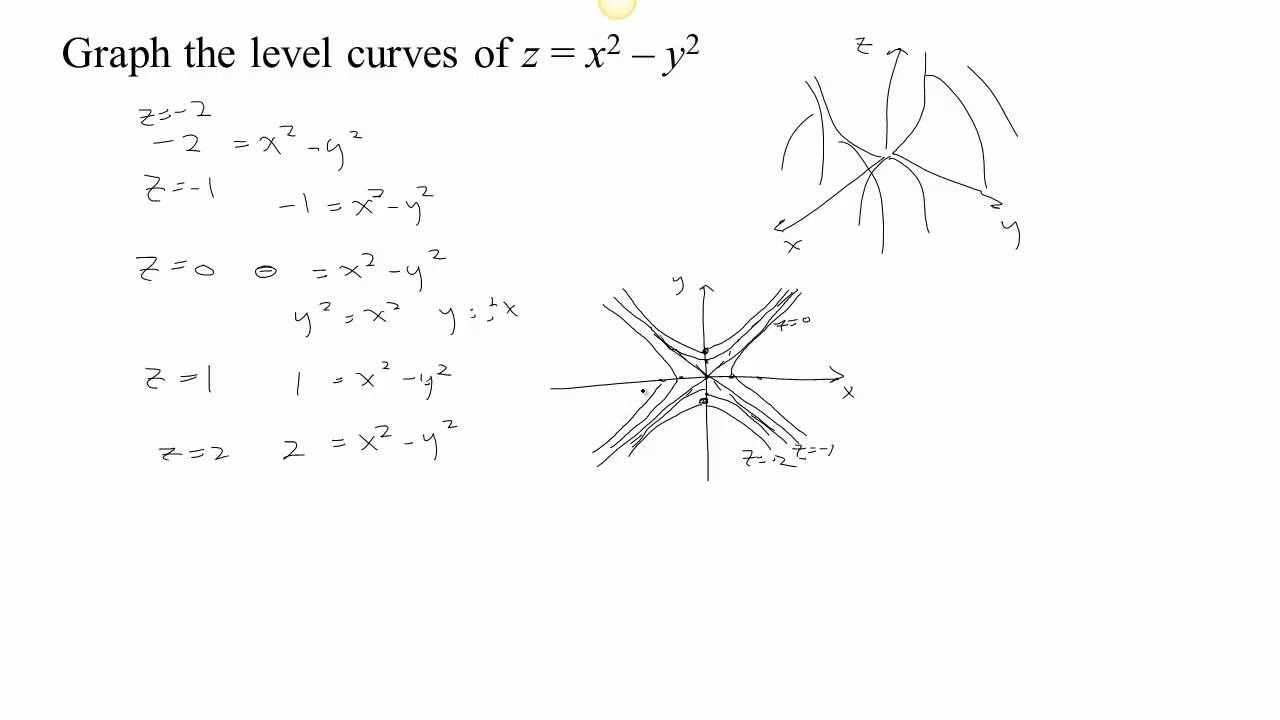



Level Curves Part 1b Hyperbolic Paraboloid Youtube
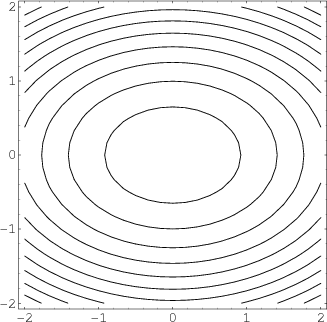



Image Elliptic Paraboloid Level Curves Math Insight
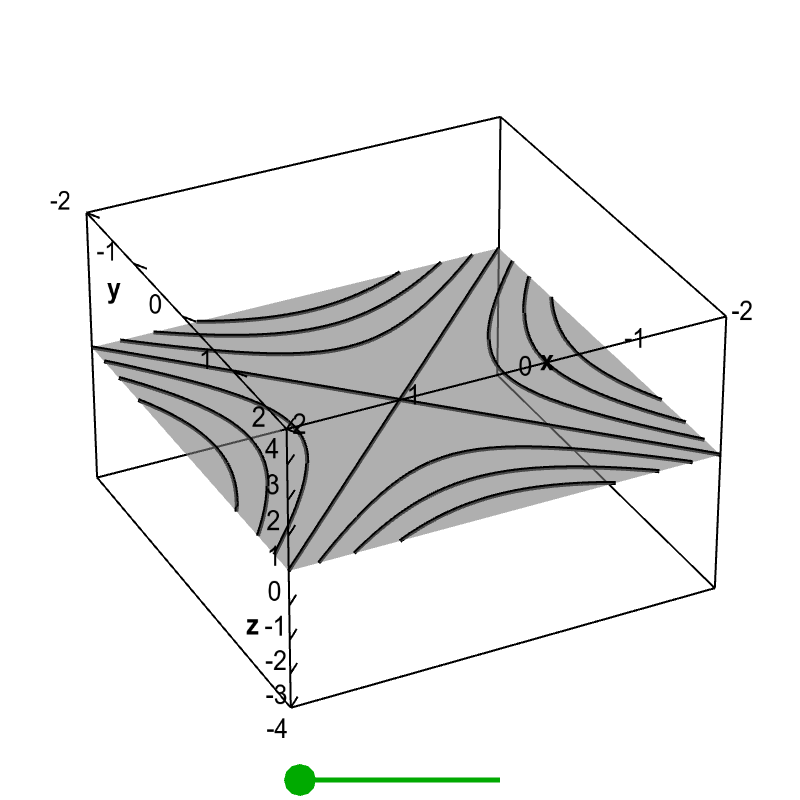



Applet Level Curves Of A Hyperbolic Paraboloid Math Insight
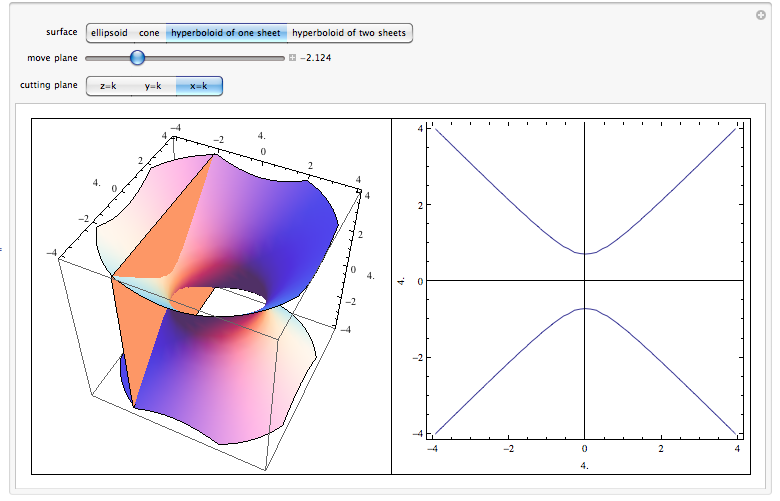



Level Surfaces




O7vwhmu1ihum



Level Curves Part 1 Elliptic Paraboloid Youtube




14 Partial Derivatives Partial Derivatives So Far We



Level Surfaces



1



2
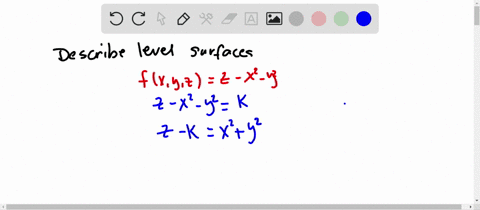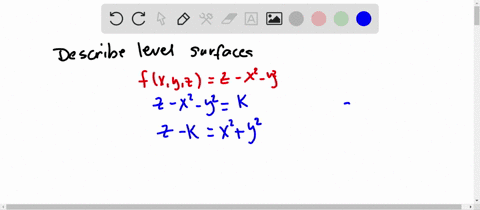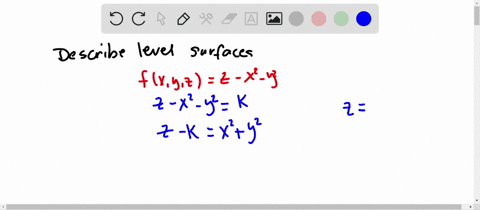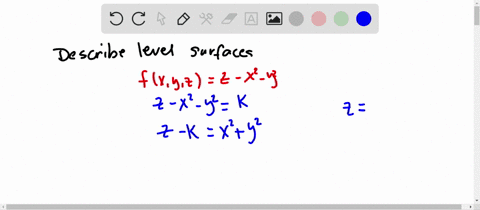



Solved Describe In Words The Level Curves Of The Paraboloid Z X 2 Y 2
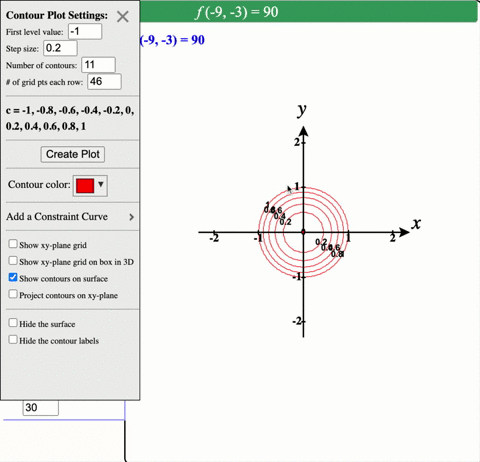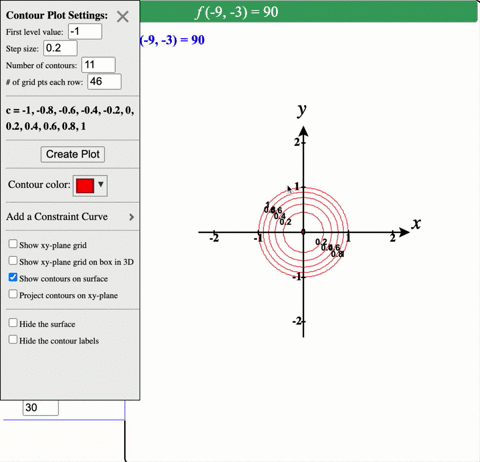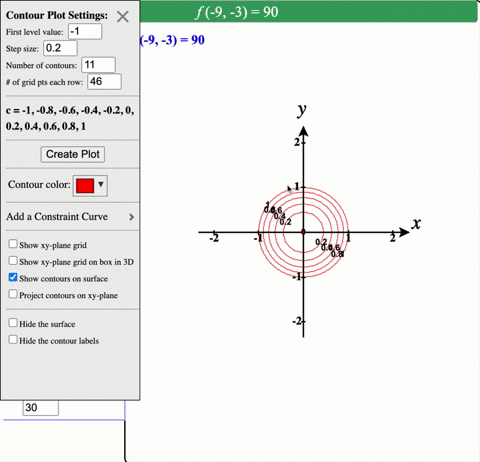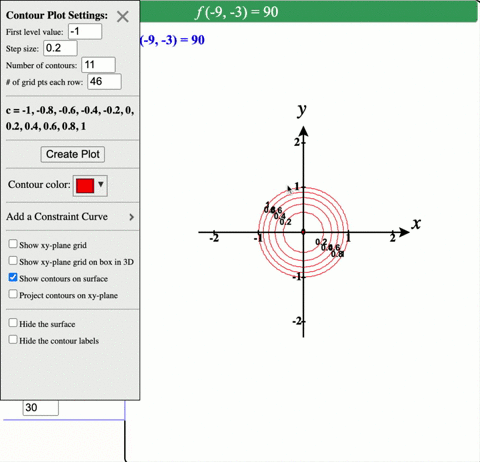



Solved Describe In Words The Level Curves Of The Paraboloid Z X 2 Y 2



Level Curves



2
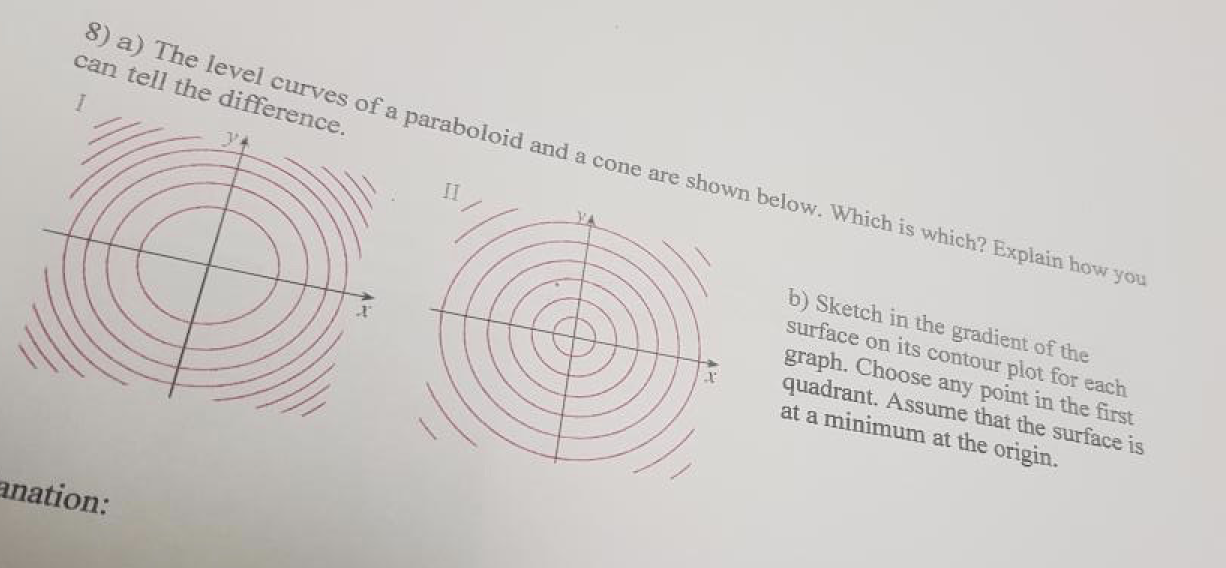



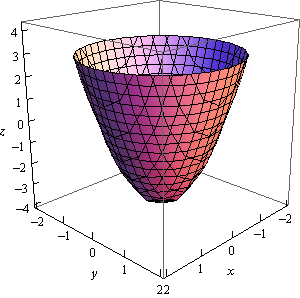
Solved 8 A The Level Curves Of A Paraboloid And A Cone Are Chegg Com




Oneclass 1 Point Match The Following Vector Fields With The Verbal Descriptions Of The Level Curve



Elementary Calculus Example 5 Same Of Hyperbolic Paraboloid



Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables




This Type Of Math Is Multivariable Calculus 1 7 Sketch The Level Curves Of F X Y P 16 X Homeworklib
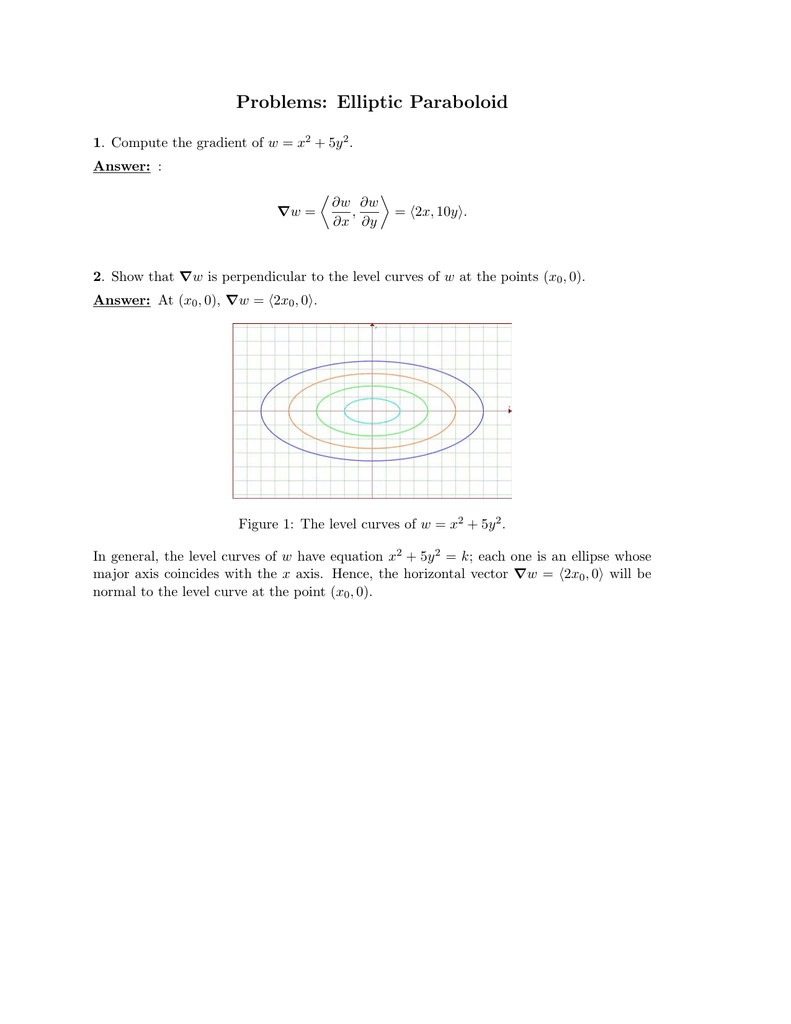



Problems Elliptic Paraboloid
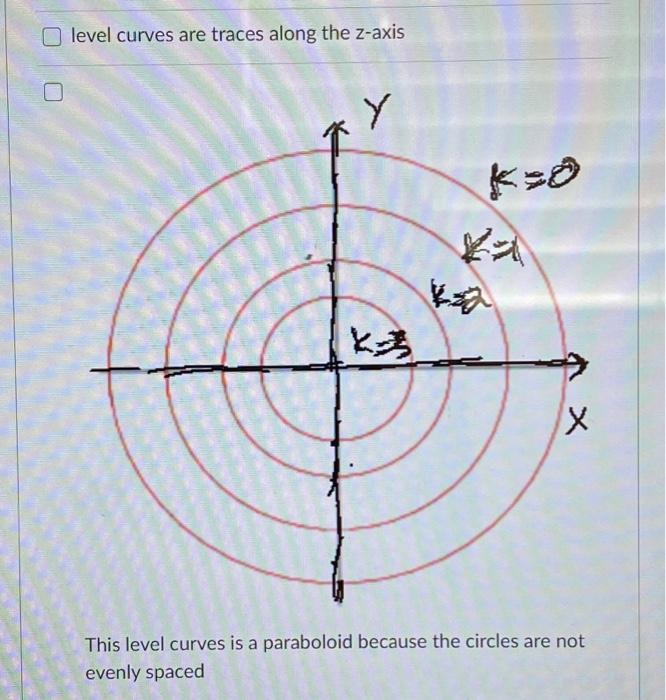



Solved Question 1 2 Pts Select All Statements That Are True Chegg Com




Paraboloid Wikipedia



Contour Maps Article Khan Academy
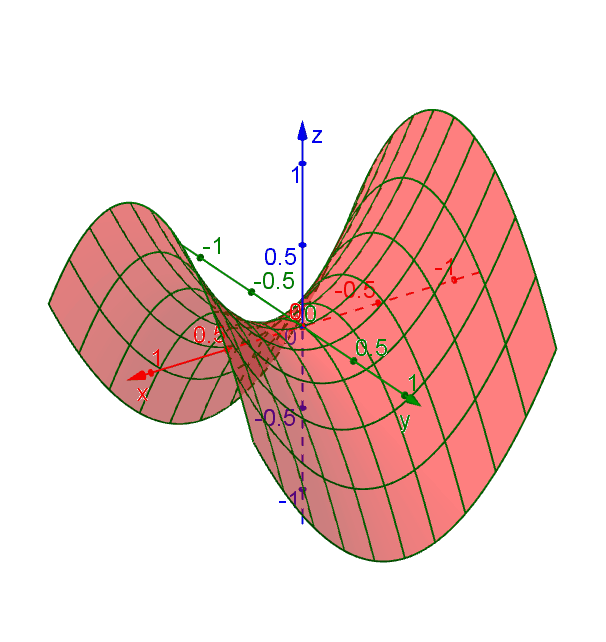



Hyperbolic Paraboloid Geogebra Dynamic Worksheet



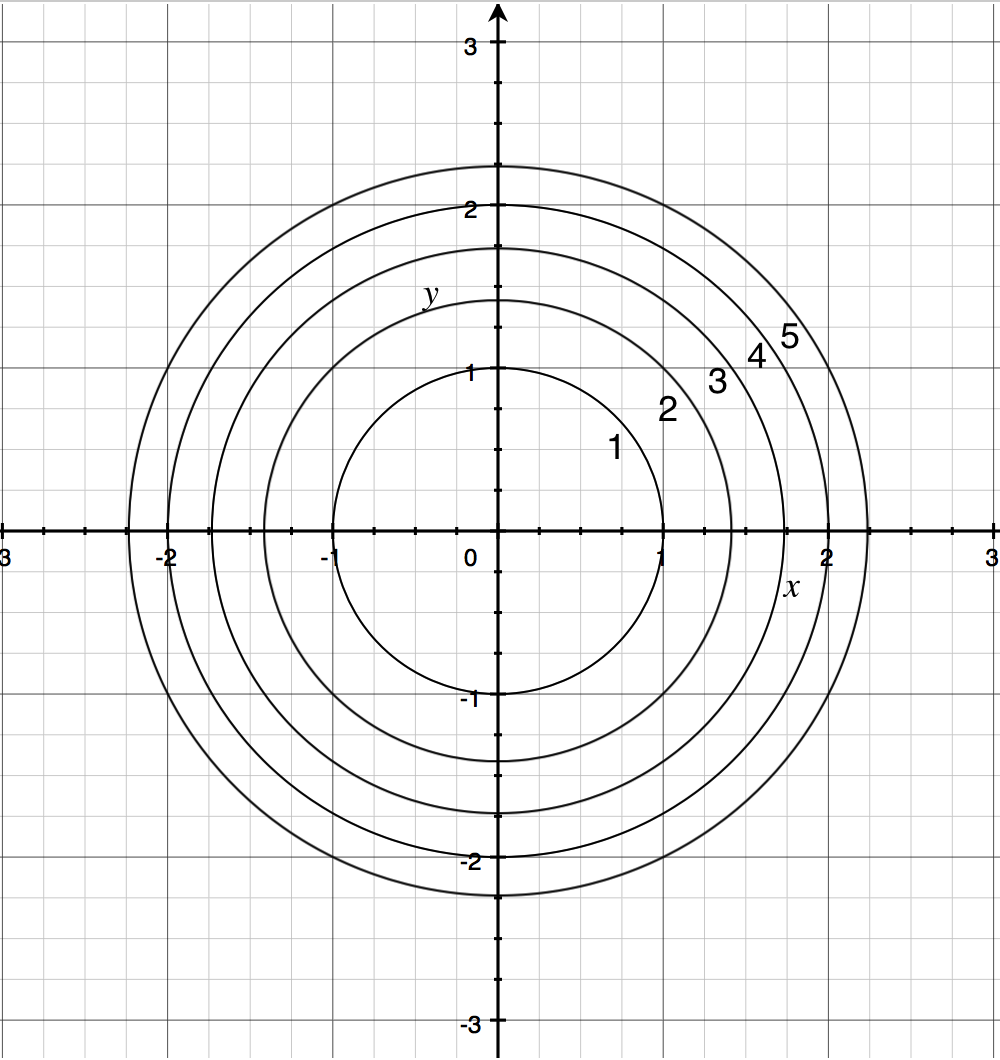
Applet Level Curves Of An Elliptic Paraboloid Shown With Graph Math Insight




Solved Level Curves Consider The Paraboloid F X Y 16 X 2 4 Y 2 16 And The Point P On The Given Level Curve Of F Compute The Slope Of The Line Tangent To The



Animated Demonstrations For Multivariable Calculus



Level Curves And Contour Plots Mathonline




Solved Iit Show Me Art Work Sketch The Level Curves For K 1 0 1 Clearly Label Theml The Surface Is 2 F 1 V 22 V Hyperbolic Paraboloid Iv Describe
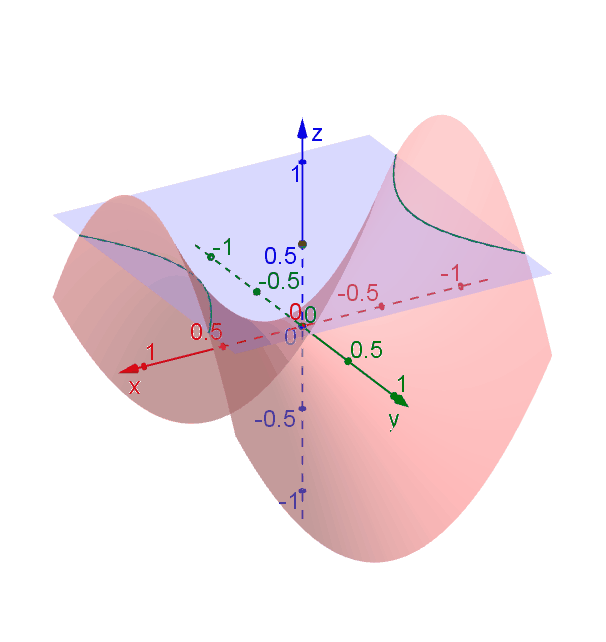



Hyperbolic Paraboloid Geogebra Dynamic Worksheet
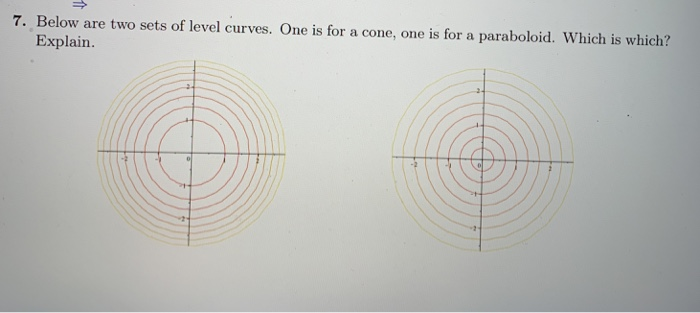



Solved 7 Below Are Two Sets Of Level Curves One Is For A Chegg Com
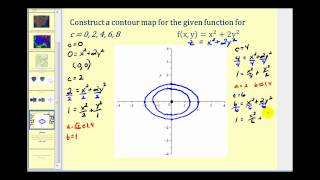



Level Curves Of Functions Of Two Variables Youtube




How To Sketch Level Curves Vector Calculus Vector Calculus Calculus Math Notes
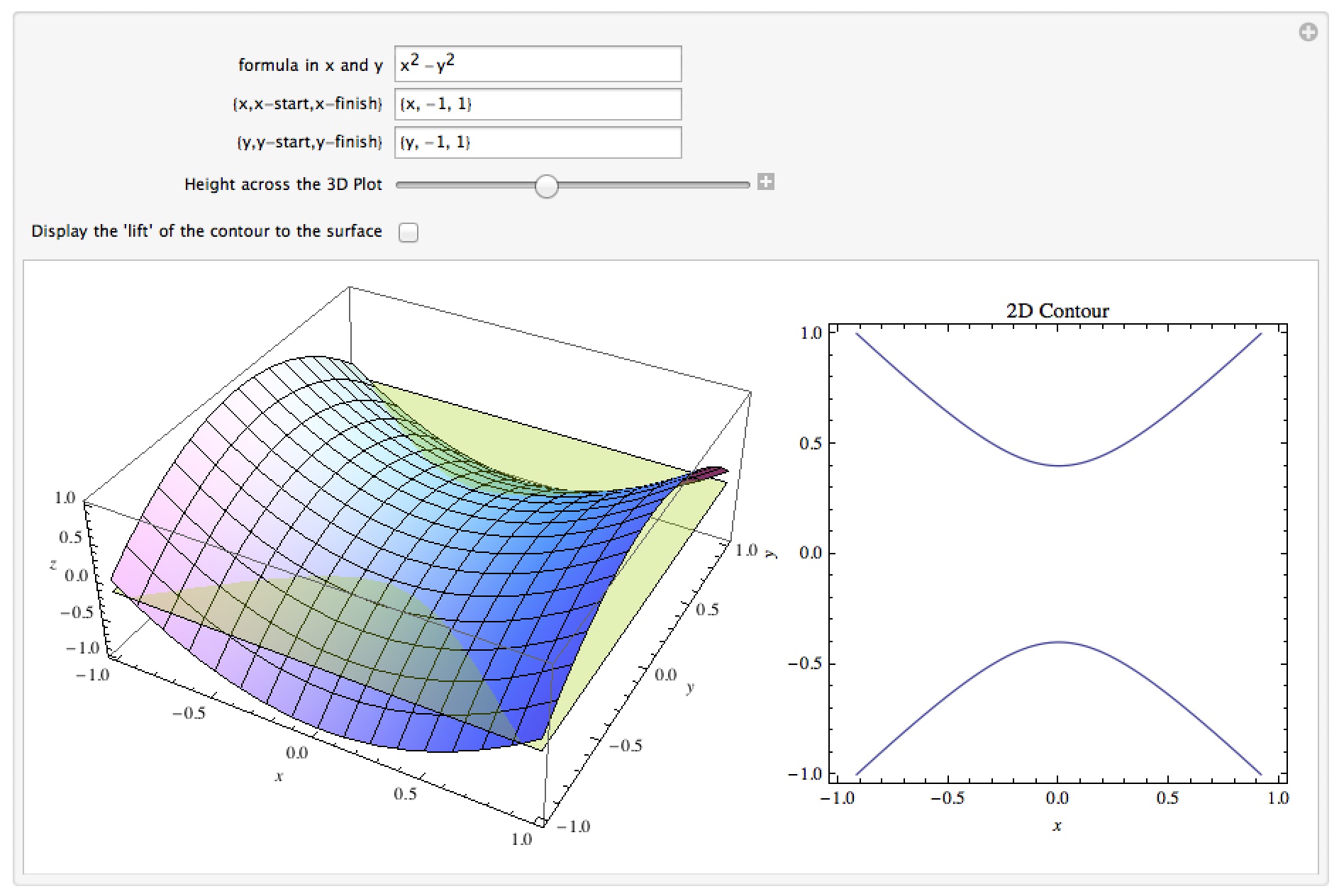



Dr Moretti S Mathematica Notebooks Calculus 3
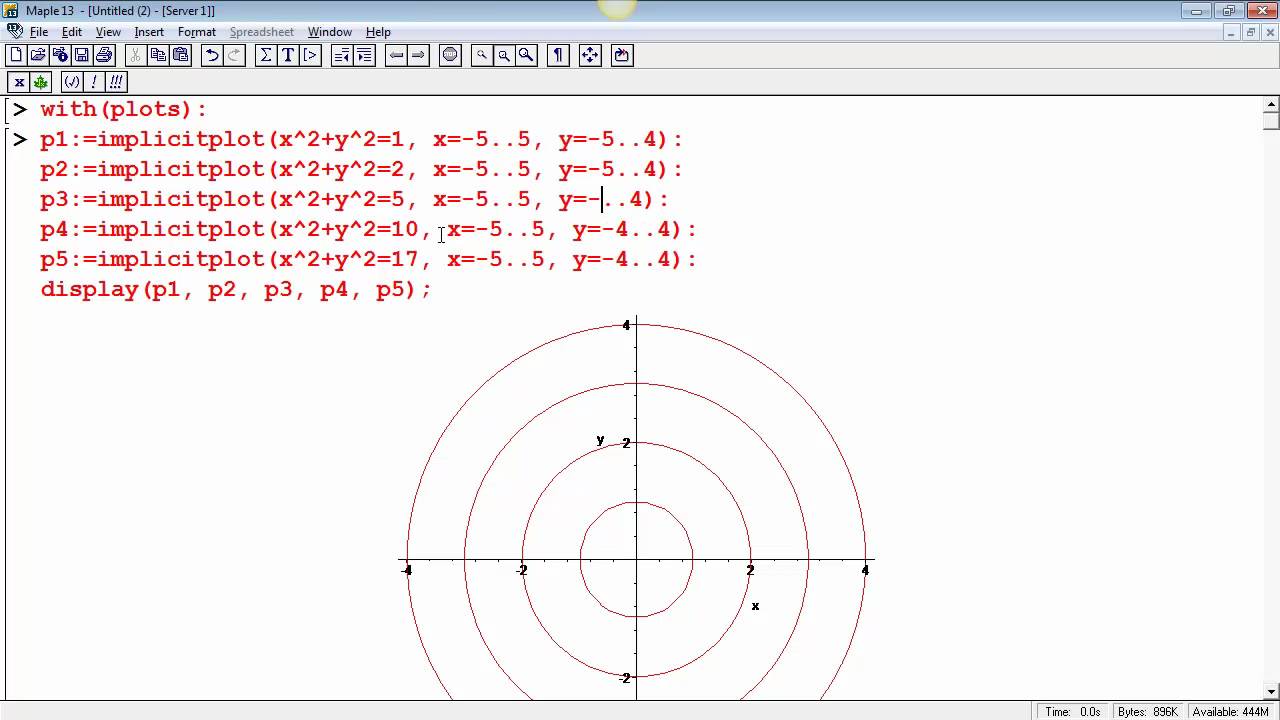



Level Curves Part 2 Cone Hyperboloid Ellipsoid Youtube



Calculus Iii 13 01 Functions With Several Variables University



Hyperbolic Paraboloid Geogebra Dynamic Worksheet




Cross Section Of The Caustic Of A Paraboloid Of Revolution In The Y 0 Download Scientific Diagram




Level Curves And Contour Maps Calculus 3 Youtube




Polar Coordinates In Tikz Addplot3 Tex Latex Stack Exchange



Latex Pictures




Session 25 Level Curves And Contour Plots Part A Functions Of Two Variables Tangent Approximation And Optimization 2 Partial Derivatives Multivariable Calculus Mathematics Mit Opencourseware



Quadric Surface The Elliptical Paraboloid Youtube



Math Colorado Edu




Paraboloid Wikipedia
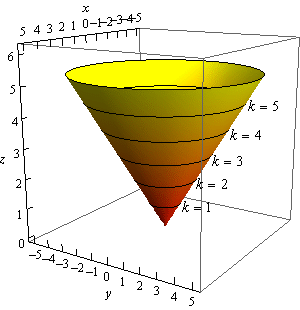



Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables



Drawing Paraboloids Ximera
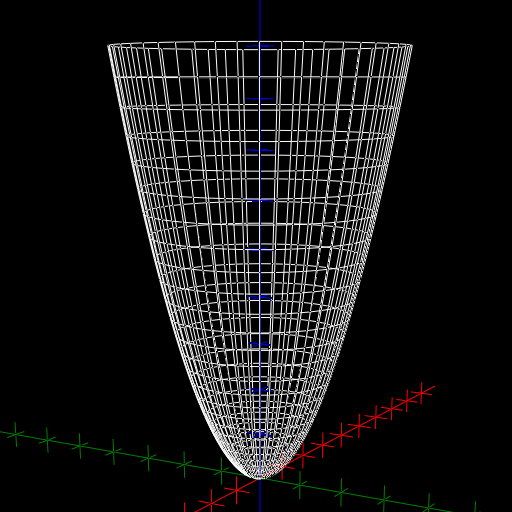



Elliptic Paraboloid The Rejbrand Encyclopaedia Of Curves And Surfaces



Level Curves And Contour Plots Mathonline



Level Sets Ximera
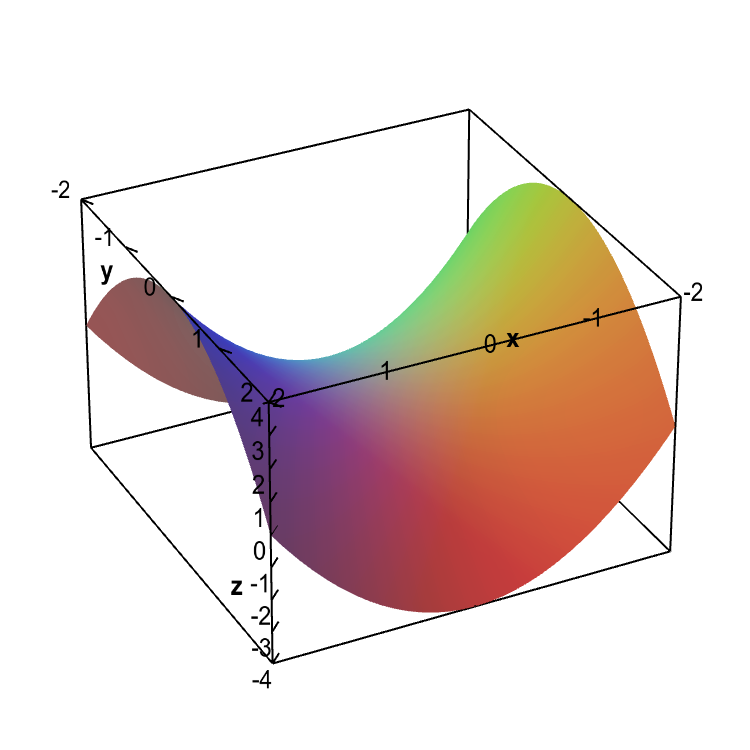



Level Set Examples Math Insight
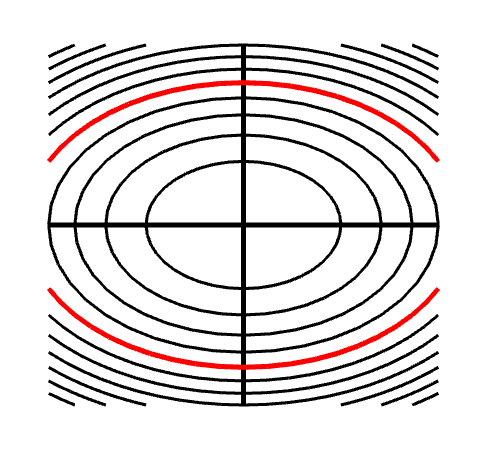



Applet Level Curves Of An Elliptic Paraboloid Shown With Graph Math Insight



Elementary Calculus Example 4 Hyperbolic Paraboloid
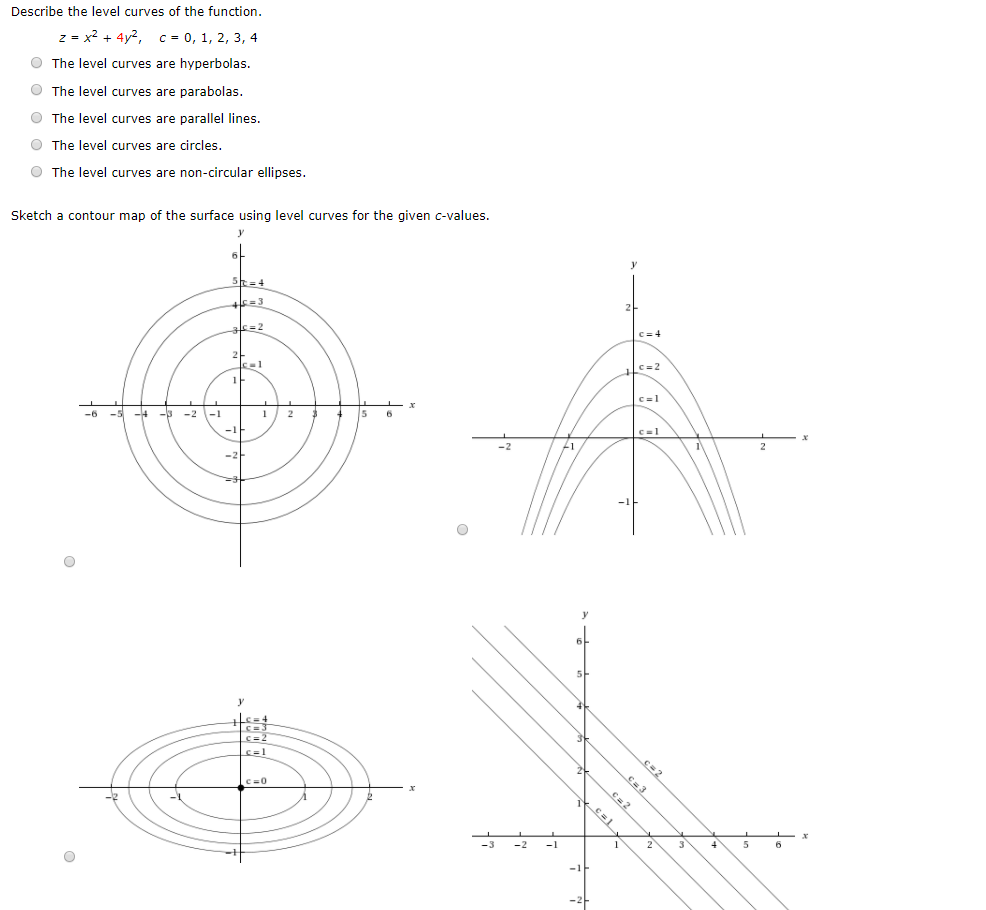



Solved Describe The Level Curves Of The Function Z X2 Chegg Com



Level Curves And Contour Plots Mathonline
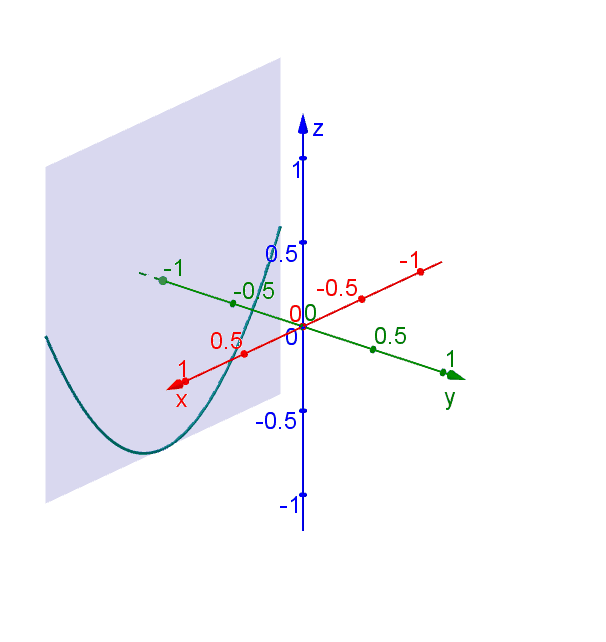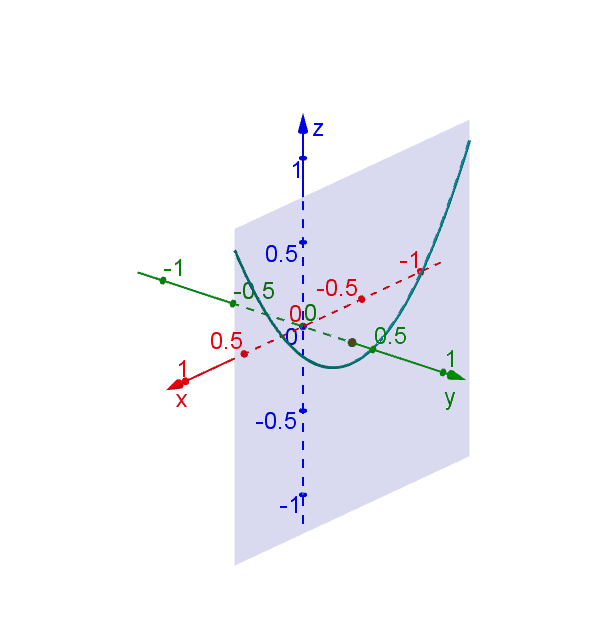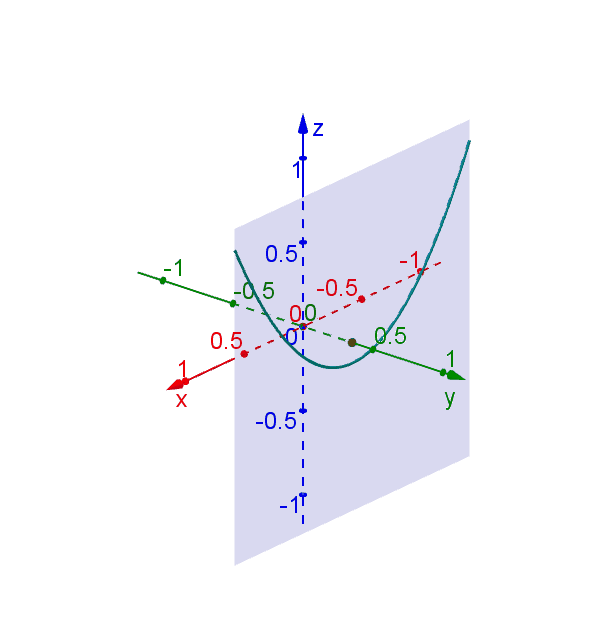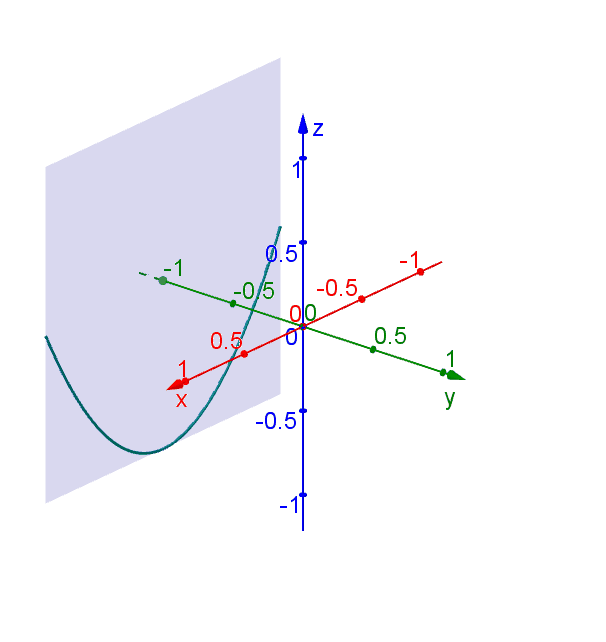



Hyperbolic Paraboloid Geogebra Dynamic Worksheet
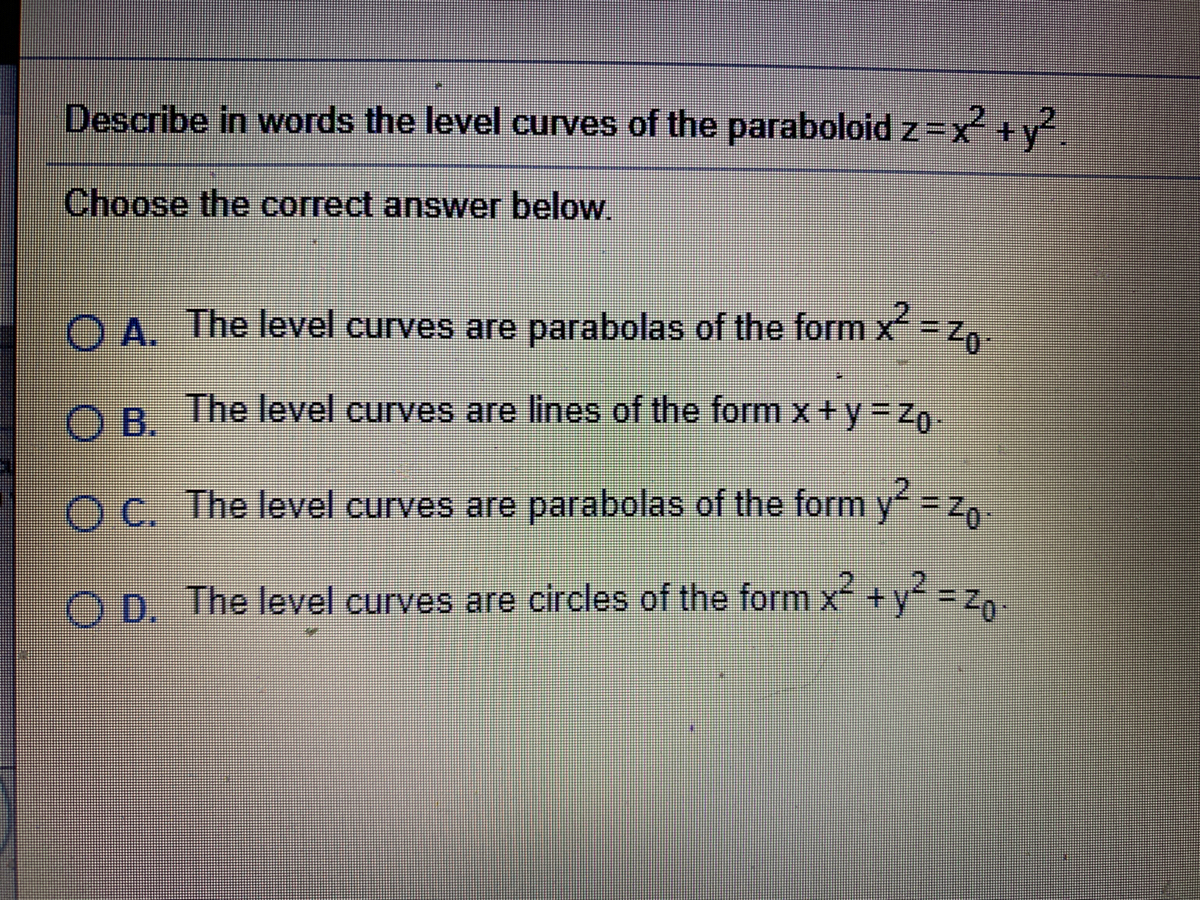



Answered Describe In Words The Level Curves Of Bartleby
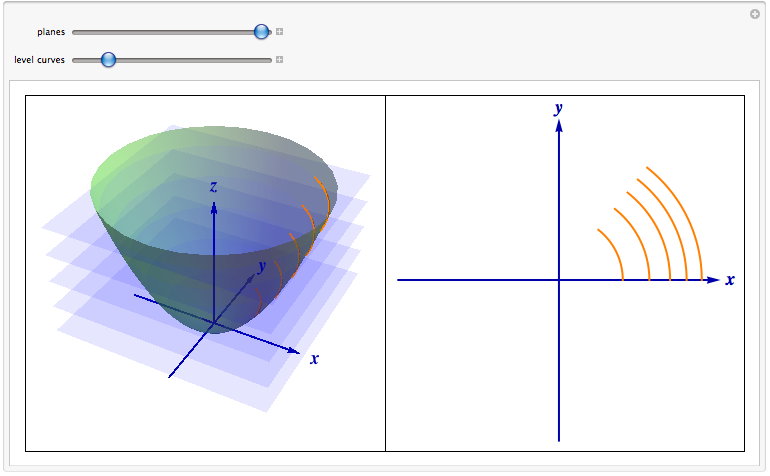



Level Curves




Session 35 Gradient Definition Perpendicular To Level Curves Part B Chain Rule Gradient And Directional Derivatives 2 Partial Derivatives Multivariable Calculus Mathematics Mit Opencourseware



0 3 Visualizing Functions Of Several Variables



Contours 3 Html




Solved Level Curves Consider The Paraboloid F X Y 16 X 2 4 Y 2 16 And The Point P On The Given Level Curve Of F Compute The Slope Of The Line Tangent To The




Functions Of Several Variables
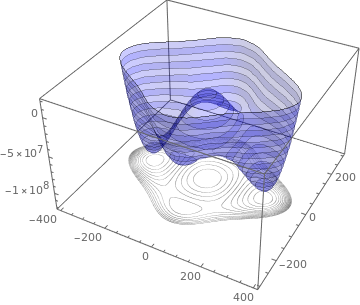



Level Sets Ximera
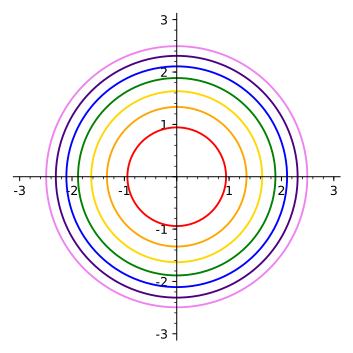



16 1 Functions Of Several Variables



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿